Setup Guide
Last Updated: Jan 08, 2026
This guide will walk you through the setup steps you need before starting Armlab.
Contents
Login to the laptop
In Armlab, each station is provided with a laptop running Ubuntu 22.04:
- If you are in the morning session, log in to student_am
- If you are in the afternoon session, log in to student_pm
Same password for both users: i<3robots!
Each laptop and its charger are labeled with a station number, do not remove the stickers. If your team is instructed to switch to a different station, please move without taking the laptops.
Please ensure that you log out of your team account when finished. Before logging out, make sure all running programs are closed and all changes are pushed to GitLab.
Fork codebase
1. Sign into Umich GitLab
The code that we will be using for this lab is hosted on GitLab. Use your laptop or the lab laptop here, go to this link and use your UM credentials to sign into your account.
For the lab laptop, use an Ethernet cable for a stable internet connection.
2. Create a Group on GitLab and Adding Members
One group member needs to create a GitLab Group and add all members. Follow these steps:
- On the left-hand menu, click on “Groups” to access the Groups page, then click the “New Group” button to initiate the group creation process.
- Group Details:
- Group name: enter
armlab-s<SECTION#>_g<GROUP #>(i.e. armlab-s012_g7) - Visibility level: select “Private”
- Leave other fields blank
- Group name: enter
- Invite your team members as “owners” of the project
- Firstly, go to groups page: sidebar -> groups
- Click your team group
- Add members: sidebar -> Manage -> Members -> invite members
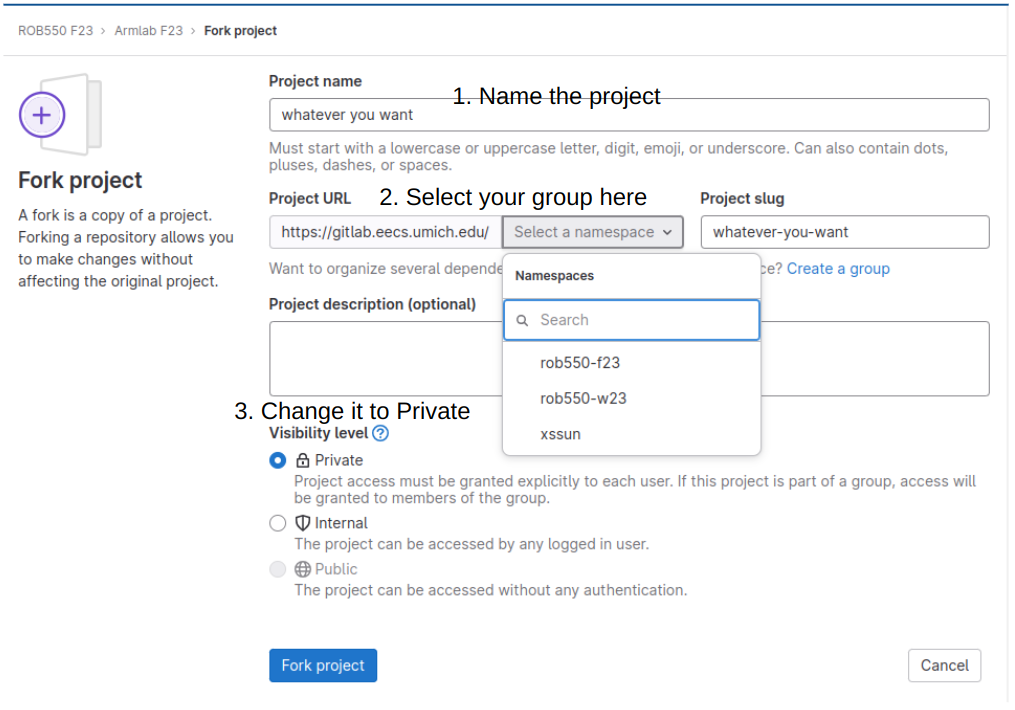
3. Fork Repositories
“Forking a repository” refers to the process of creating a personal copy of a repository (a collection of files and code) hosted on a platform like GitHub or GitLab, in our case is GitLab. This copy is entirely separate from the original repository, allowing you to make changes and updates without affecting the original project. In order to create a fork, complete the following steps:
- Navigate to the repository you’d like to fork, in this case, you should fork the armlab’s repository
- On the top right, select “Fork”
- You can change the name of the repository if you would like, but the key thing is to change the “Project URL” field so that it is forked into the group you just created.
-
Change the visibility level to “Private”.
4. Clone to local
-
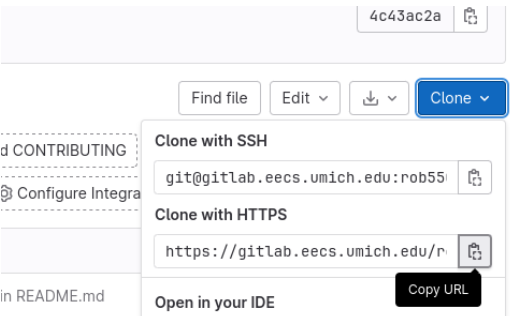
Go to your group’s armlab repository webpage and copy the URL of “Clone with HTTPS”
- On the lab laptop, open a Terminal (shortcut: ctrl+alt+t), run the following commands:
# move to home directory cd ~ # clone the codebase to your laptop git clone https://your_groups_url- To copy-paste anything in the terminal, we can use
ctrl+shift+c/ctrl+shift+v - The
git clonecommand will prompt you for a username and password. Please enter your UMICH credentials.
The repo must be cloned to the home directory
~. If you clone your armlab repo into a subfolder you will not be able to run the control station! - To copy-paste anything in the terminal, we can use
- After cloning the code, enter this command in the terminal to see the cloned directory:
# ls will show all the files/folders under the current directory lsThe commands we use here are known as Linux command line tools. Understanding the basics of Linux CLT is essential for smooth progress in this class. If you are not familiar with it, this post provides some basic information you need to know.
At this point, you should have your team forked Armlab codebase and cloned it on the Ubuntu laptop at your team’s station.
Installation
To use the code, firstly, we need to install all the dependencies/SDKs we need.
1. Install all the dependencies and packages
If this is your first time setting up, you need to install the necessary dependencies and packages. Open a terminal and navigate to folder /install_scripts. Then, run the following command:
./install_Dependencies.sh
- Tip: The “TAB” key is a handy tool for auto-completing your input commands. For instance, try typing “./install_De” and then press the “TAB” key. This should automatically complete the rest of the command for you.
- Note: If the auto-complete feature does not work, it often indicates insufficient permissions for the install script file, which may also prevent the file from running. To address this, grant the necessary permissions using the command:
chmod +x ./install_Dependencies.sh
Wait until it’s complete before proceeding to the next step.
2. Install interbotix arm
Run the following command:
./install_Interbotix.sh
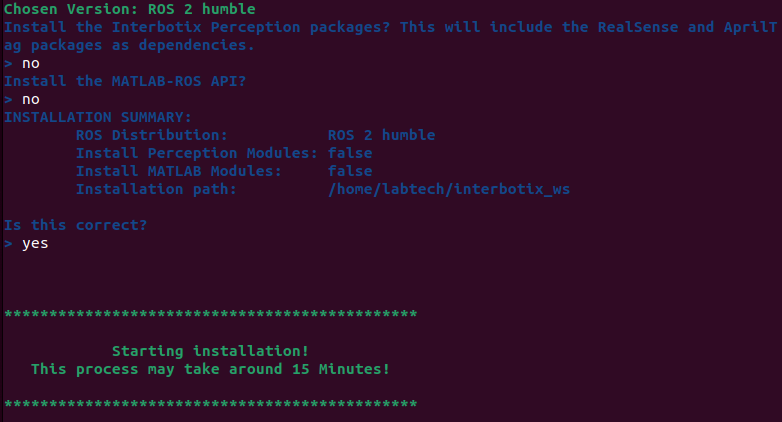
During the installation, you’ll encounter prompts. For prompts related to AprilTag and MATLAB-ROS installation, type no and press Enter.
Be cautious with the prompts and enter exactly what is specified in the image. We install the perception module separately. If you enter ‘Yes’ to the perceptoin module, it will result in the installation of a duplicate AprilTag module, leading to configuration issues.
Wait until it’s complete before proceeding to the next step.
3. Move config files
Run the following command:
./install_LaunchFiles.sh
- This file is used to move the config files. The configurations are based on the AprilTag family we have and the specific camera model we use.
4. Install camera calibration package
Open a NEW terminal window to run the following command. If you use an existing terminal, the installation will fail.
./install_Calibration.sh
Wait until it’s complete before proceeding to the next step.
5. Set up ROS_DOMAIN_ID
Run the following command:
echo "export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=your_station_number" >> ~/.bashrc
- Note, replace
your_station_numberwith the actual number on the wall next to your station’s desk. For example station 1 should have:echo "export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=1" >> ~/.bashrc - Set up ROS_DOMAIN_ID is crucial. Ensure it’s done correctly to prevent chaos in the lab.
- To check if you set it successfully, open a new terminal and run:
printenv | grep ROS- where you should see the output has all the environmental variables related to ROS, and you should see ROS_DOMAIN_ID=the_number_you_set print out in the terminal
6. Reboot
If you have successfully completed all the steps above, please reboot the computer.
sudo reboot
Testing
After successfully installing all the necessary components for the workstation, now it is time to test.
To launch everything
First, connect the camera USB and arm USB to the lab laptop, then open a terminal and navigate to the folder /launch. Run the provided command. Remember that to halt any node, use ctrl + C in its respective terminal. Until you stop this node, the terminal will be occupied. If you need to run another command, open a new terminal.
./launch_armlab.sh
- This one starts all 3 nodes we need: camera, apriltag, interbotix_arm.
Then in a new terminal, run the following command:
./launch_control_station.sh
- This one starts the control station GUI.
- To stop the control station, you just need to close the GUI window.
These two .sh files combine multiple single-line commands that we need to start the project, making it simpler to initiate everything from a single location and with fewer open windows.
Result
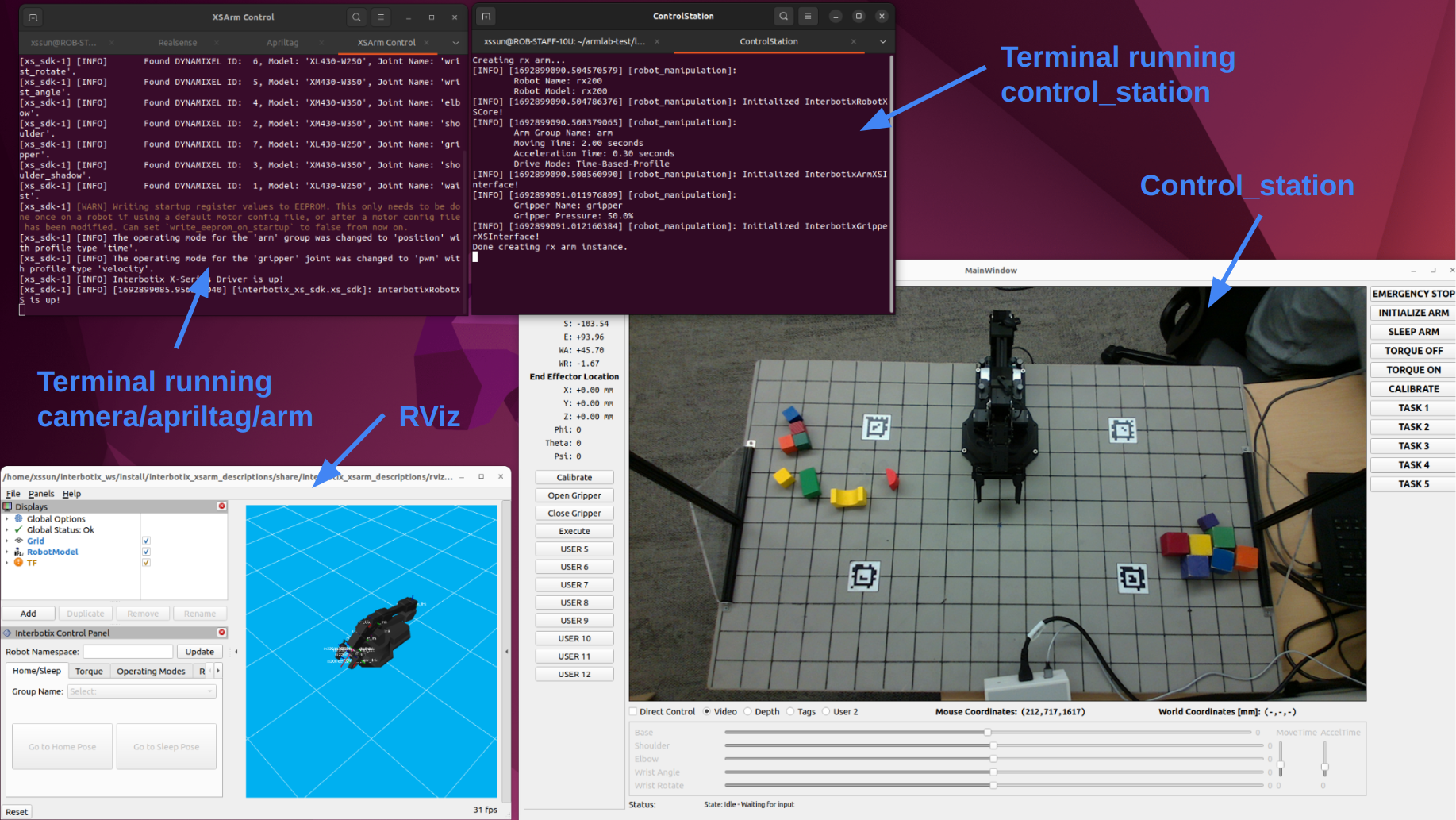
By launching all the ROS nodes we need, you are starting the camera, the apriltag package, and the arm, along with a control station GUI where you can manually control the arm. We will talk about how to control the arm later in the checkpoint 1.
If you launch everything successfully, this will be the scene on your laptop:
- To quit control station, click the “exit” button on the top right corner
- To quit other nodes, hit ctrl+c in the terminal
Always put the arm in the sleep position when you stop using the arm node!
Otherwise the arm loses torque will then splash on the board : D
At this stage, you should have the nodes and control station GUI launched, indicating that you have completed the setup for Armlab. You can now proceed to the checkpoints if you wish.